- The atomic weight is estimated from the atomic mass of isotopes of an element. It is determined from the atomic number and the mass number. It is the sum of the mass of electrons, protons, and neutrons present in an atom. The atomic weight depends on the relative abundance of isotopes of an element in a given sample.
- Atomic weight, also called relative atomic mass, ratio of the average mass of a chemical element ’s atoms to some standard. Since 1961 the standard unit of atomic mass has been one-twelfth the mass of an atom of the isotope carbon-12.
Standard atomic weights 2013 abridged to five significant digits. Slither.io. Portal flashclout games. Atomic weights are scaled to A r (12 C)=12, where 12 C is a neutral atom in its nuclear and electronic ground state. The atomic weights of many elements are not invariant, but depend on the origin and treatment of the material.
Also found in: Thesaurus, Medical, Encyclopedia.Related to Atomic weights: nuclear atom
atomic weight
n. The average mass of an atom of an element, usually expressed relative to the mass of carbon 12, which is assigned 12 atomic mass units.
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
atomic weight
n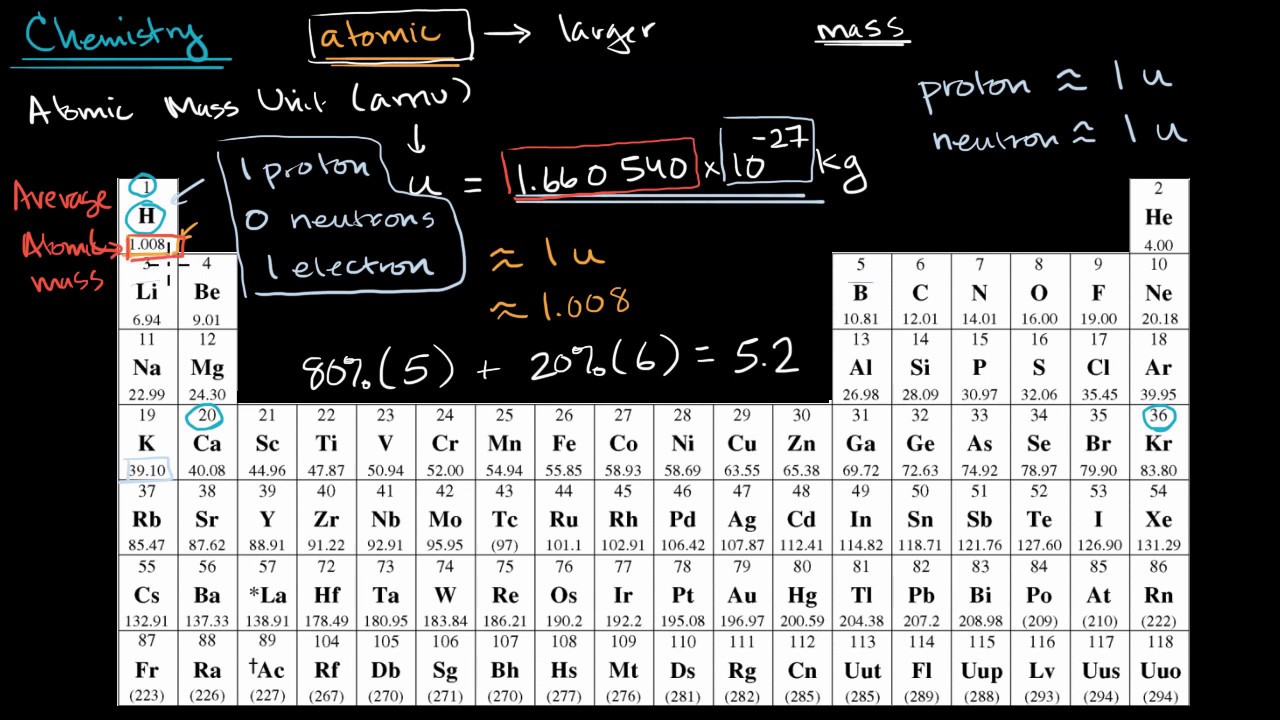
(Chemistry) the former name for relative atomic massAbbreviation: at wt
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
atom′ic weight′

Atomic Weights Of Compounds
n.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/PeriodicTableoftheElements-5c3648e546e0fb0001ba3a0a.jpg)
the average weight of an atom of an element, based on 1/12 the weight of the carbon-12 atom. Abbr.:at. wt.
Random House Kernerman Webster's College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
atomic weight
The average mass of a chemical element, expressed in atomic mass units. The atomic weight of an element having more than one principal isotope is calculated both from the atomic masses of the isotopes and from the relative abundance of each isotope in nature. For example, the atomic weight of the element chlorine is 35.453, determined by averaging the atomic masses and relative abundances of its two main naturally occurring isotopes, which have atomic masses of about 35 and 37. Compare atomic mass.
The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. Copyright © 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
| Noun | 1. | atomic weight - (chemistry) the mass of an atom of a chemical element expressed in atomic mass units atomic mass, relative atomic mass mass - the property of a body that causes it to have weight in a gravitational field combining weight, eq, equivalent weight, equivalent - the atomic weight of an element that has the same combining capacity as a given weight of another element; the standard is 8 for oxygen meq, milliequivalent - one-thousandth of an equivalent chemical science, chemistry - the science of matter; the branch of the natural sciences dealing with the composition of substances and their properties and reactions |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.
Atomic Weight Of Copper
Want to thank TFD for its existence? Tell a friend about us, add a link to this page, or visit the webmaster's page for free fun content.Link to this page:
Atomic Weights List
